Where Do Axolotls Live

Where Do Axolotls Live?
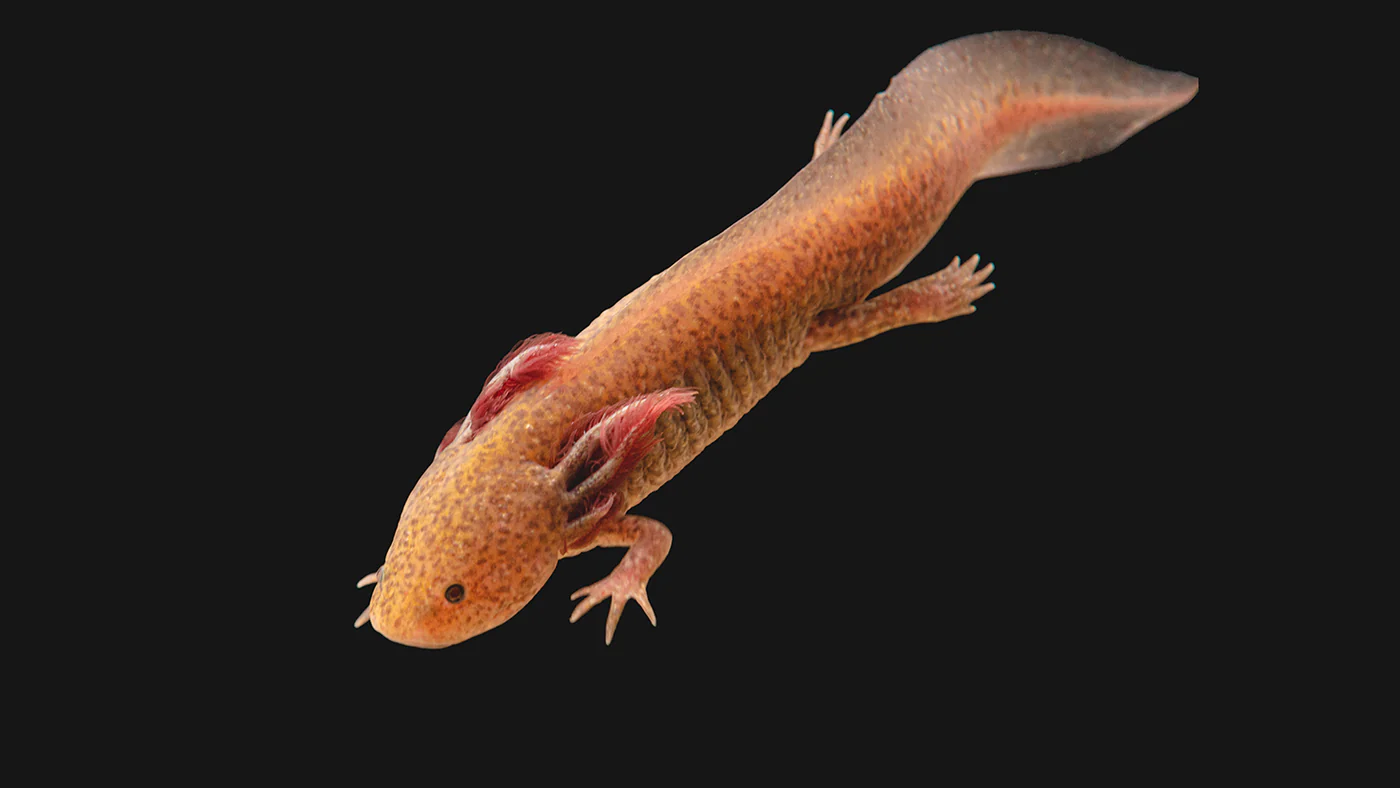
The axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) is a unique amphibian that has garnered attention for its incredible regenerative abilities and distinctive appearance. Native to Mexico, these fascinating creatures inhabit a specific range that reflects their ecological needs and adaptations. In this blog post, we will explore the natural habitat of axolotls, their current conservation status, and the importance of their environment.
Natural Habitat
Axolotls are primarily found in the remnants of the ancient lake complex of Xochimilco, located near Mexico City. Historically, this area was a vast network of lakes and canals, providing an ideal environment for these aquatic creatures. Today, however, the axolotl’s habitat has diminished significantly due to urbanization, pollution, and agricultural activities. What Do Axolotls Eat
1. Aquatic Environment
Axolotls thrive in freshwater lakes, canals, and ponds. They prefer shallow waters with plenty of vegetation, where they can find shelter and food. The presence of aquatic plants is crucial as they offer hiding spots from predators and help maintain water quality by absorbing excess nutrients.
2. Temperature and Water Conditions
The typical water temperature for axolotls ranges from 60°F to 68°F (15°C to 20°C). They are sensitive to temperature fluctuations, and their habitat should ideally have a stable environment. Additionally, axolotls prefer slightly acidic to neutral water, with a pH level between 6.5 and 8.0.

Current Distribution and Habitat Loss
Despite their once widespread presence, axolotls are now critically endangered. The primary factors contributing to their decline include:
- Urban Development: The expansion of Mexico City has led to the destruction of natural habitats, with many lakes and canals being drained or filled for construction.
- Pollution: Agricultural runoff and urban waste have contaminated the remaining water bodies, negatively affecting water quality and the overall ecosystem.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species, such as carp and tilapia, has increased competition for resources and predation on axolotls.
1. Conservation Efforts
Efforts are underway to conserve the axolotl and its habitat. Organizations and scientists are working on breeding programs, habitat restoration, and raising public awareness about the importance of protecting this unique species. Conservation areas have been established in Xochimilco to preserve the remaining populations and their environment. axolotl for sale
2. Captive Breeding
Many axolotls are now bred in captivity for research and the pet trade. While this helps to alleviate pressure on wild populations, it also raises questions about genetic diversity and the long-term viability of these captive populations. Where Do Axolotls Live
Conclusion
Axolotls are not just intriguing creatures; they are a vital part of their ecosystem and an indicator of environmental health. Their native habitat in Xochimilco is under threat, making conservation efforts critically important. By understanding where axolotls live and the challenges they face, we can better appreciate these remarkable amphibians and work towards ensuring their survival for future generations. Whether in the wild or in captivity, axolotls continue to inspire awe and curiosity, reminding us of the delicate balance of nature and the importance of preserving it.